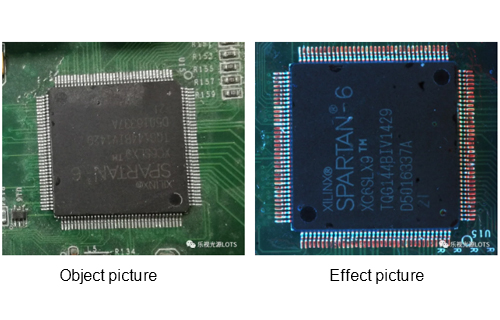
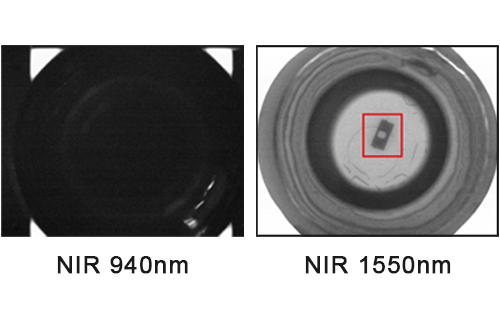
In modern automated production processes, machine vision has begun to slowly replace artificial vision, especially in the fields of working condition detection, finished product inspection, quality control, etc., and is widely used. With the advent of the Industrial 4.0 era, this trend is irreversible.
Machine vision is a device that automatically receives and processes an image of a real object through optical devices and non-contact sensors to obtain the required information or to control the movement of a robot.
Machine vision is the use of machines to replace human eyes for measurement and judgment. In essence, machine vision is the application of image analysis technology in factory automation. It uses optical systems, industrial digital cameras and image processing tools to simulate human visual capabilities and make corresponding decisions, and finally executes these decisions by commanding a specific device.
Why should machine vision replace artificial vision?
There are many reasons. The following are the main ones: 1. From the perspective of production efficiency, since operators are easily tired after working for a long time, the quality of artificial vision is low and the accuracy is not high, while machine vision can greatly improve production efficiency and automation.
2. From the perspective of cost control, training a qualified operator requires a lot of manpower and material resources for enterprise managers. However, simple training is far from enough. It will take a lot of time to improve the operator's level in practice. As long as the machine vision system is properly designed, debugged and operated, it can be used uninterruptedly for a long time while ensuring production results.
3. When implementing working condition detection in certain special industrial environments, such as welding and gunpowder manufacturing, artificial vision may pose a threat to the personal safety of operators, while machine vision effectively avoids these risks to some extent.
What fields does machine vision cover?
A machine vision system is composed of different functional modules. Designing a successful machine vision system requires high standards from engineers.
Generally speaking, the professional fields covered by machine vision are as follows:
1. Electrical engineering: used for the design of hardware and software in machine vision systems.
2. Engineering mathematics: the basis of image processing technology.
3. Physics: the basis of lighting system design.
4. Mechanical engineering: the most widely used application of machine vision systems. A good machine vision system can better provide the manufacturing industry with more technical support that is conducive to improving product quality and production efficiency.
Modules that make up a machine vision system
A complete machine vision system is generally composed of optical systems (light source, lens, industrial camera), image acquisition units, image processing units, actuators, and human-machine interfaces. All functional modules complement each other and are indispensable.
Lighting (light source)
Lighting is an important factor affecting the input of the machine vision system. The design of the light source system is crucial and directly related to the input data, that is, the quality of the image and the application effect.
Engineers need to first determine effective lighting conditions and select appropriate lighting devices based on user needs and product characteristics to ensure that the images generated under these lighting conditions can highlight the target information features required by users.
Light sources are generally divided into visible light sources and invisible light sources. Visible light sources commonly used in industry include LEDs, halogen lamps, fluorescent lamps, etc.; invisible light sources mainly include near-infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, etc.
LED light source is currently the most widely used machine vision light source. It has the characteristics of high efficiency, long life, moisture resistance and shock resistance, energy saving and environmental protection. It is the best choice for engineers when designing lighting systems.
Invisible light sources are mainly used to meet some specific needs, such as the inspection of pipeline welding processes. Due to the penetrability of invisible light, it can reach the inspection point.
Lens
The lens is an important component in the machine vision system, and its function is optical imaging.
The main parameters of the lens include focal length, depth of field (DOF), resolution, working distance, field of view (FOV), etc.
Depth of field refers to the range of distances of the subject before and after the best focus when the lens can obtain the best image.
Field of view refers to the maximum range that a camera can observe, usually expressed in angles. Generally speaking, the larger the field of view, the larger the observation range.
Working distance refers to the distance from the lens to the subject. The longer the working distance, the higher the cost.
When designing a machine vision system, choose lenses whose parameters match the user's needs.
Industrial cameras
Industrial cameras are essential in machine vision systems. They are used to capture images just like human eyes. Cameras can be divided into CCD cameras and CMOS cameras according to their photoreceptors.
CCD—Charge Coupled Device
CMOS —Complementary MetalOxide Semiconductor
CCD cameras are more expensive, but their image quality, image transparency, and color richness are much better than CMOS cameras.
CCD cameras can be divided into two categories: linear array and area array according to the CCD photosensitive elements they use.
Linear array cameras are in the shape of "lines" and can only process image information in units of lines. They have high resolution and fast speed. They are mainly used in matching machine vision systems in the fields of industry, medical treatment, scientific research, etc.
Area array cameras can obtain information about the entire image at one time and are relatively cheap.
Image acquisition unit
The most important component in the image acquisition unit is the image acquisition card, which is the interface between the image acquisition unit and the image processing unit. It is used to digitize the acquired images and input and store them in the computer. The image processing unit contains a large number of image processing algorithms. After acquiring the image, these algorithms are used to process the digital image, analyze and calculate, and output the results.
Actuator and human-machine interface
After completing the image acquisition and processing, the image processing results need to be output and actions matching the results need to be taken, such as rejecting waste, alarming, etc., and production information needs to be displayed through the human-machine interface.
The principle of machine vision system
The target to be photographed is converted into an image signal through the optical system, and then the image signal is transmitted to the image acquisition card and converted into a digital signal based on pixel distribution, brightness, color and other information.
The image processing unit effectively operates on these digital signals and obtains the characteristic values of the photographed target, thereby directing the device to perform corresponding actions according to the results of the discrimination.