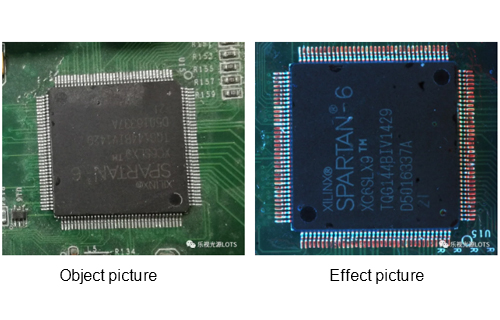
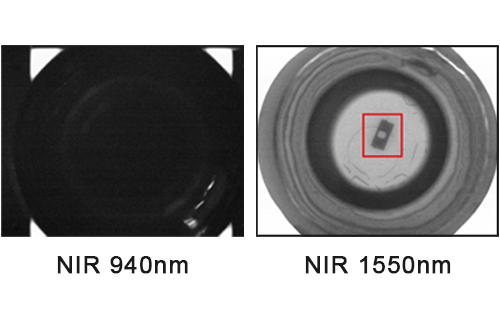
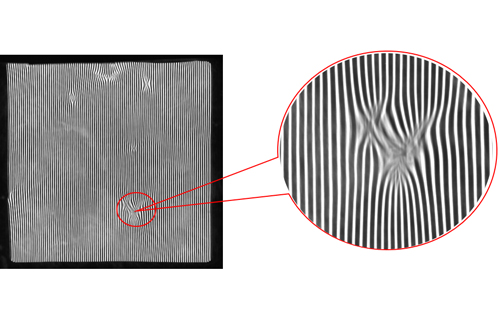
As a common industrial camera, line array cameras mainly use a single beam of scanning light to scan objects. The objects to be inspected usually move at a constant speed, and one or more cameras are used to scan them line by line continuously to achieve uniform detection of their entire surface.
From the above picture, we can see the product style of the linear array industrial camera, which is a line in the middle. Line scan camera: As the name suggests, the scan is in the shape of a "line". Although it is also a two-dimensional image, it is several K long and only a few pixels wide.
Why do you need a line scan camera?
There are many reasons and scenarios for customers to use line scan cameras, which can be summarized into the following three factors:
1. The particularity of the object being photographed
• Moving, infinitely long objects, such as cloth, steel belts, film materials, and paper
• Products of different sizes, colors, and distributions on the conveyor belt: fruits and vegetables, minerals, metal parts, etc.
• Cylindrical objects: cans, roller devices
2. High requirements for light uniformity
• Linear array light sources are easier to achieve uniform lighting than area array light sources
3. Cost considerations
• 1 linear array camera vs. multiple area array cameras: lower cost and easier deployment.
• Linear array camera vs. high-resolution area array camera: lower cost. For example, in the high-resolution flat panel inspection industry, the cost of using a high-resolution area array camera is very high, while the cost of using a linear array camera can be much lower. At the same time, the appearance of the screen is also very friendly to the linear array camera: the length and width are uniform. The linear array camera scans from top to bottom to achieve the imaging effect of a high-resolution area array camera.
Classification of Linear Array Cameras
1. According to the chip type, it can be divided into CCD cameras (mainstream) and CMOS cameras.
2. According to the different linear array image sensors, it can be divided into monochrome cameras and color cameras.
3. According to the scanning lines, it can be divided into single-line, dual-line, triple-line, multi-line and other types.
Application Industry
Line scanning system has good application in large format, high precision, cylindrical object detection, etc. The main application industries are: printed products, large glass, LCD panel detection, PCB detection, steel detection, grain color sorting, tobacco industry, textile industry, etc. Their common characteristics are wide format, fast speed, high precision, and high continuity of products on the assembly line.
Working principle of line array camera
Each time the camera is exposed, the CMOS sensor in the line array camera takes a picture of a line passing through the camera working area. The object being photographed continuously passes through the camera to complete the image acquisition of the entire product. The final output image is processed from the images taken by the CMOS chip with 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 or 16 lines.

Advantages and disadvantages of linear array cameras
1. Advantages
• Flexible pixel size and high frame rate, especially suitable for measuring one-dimensional dynamic targets.
• High resolution of linear array, which can meet most measurement site requirements.
2. Disadvantages To obtain a two-dimensional image with a linear array, a scanning motion must be used. In addition, in order to determine the corresponding position of each pixel of the image on the object under test, a grating or other device must be used to record the coordinates of each scanning line of the linear array. Generally speaking, these two requirements lead to the following disadvantages in obtaining images with a linear array:
• Long image acquisition time and low measurement efficiency.
• The existence of scanning motion and corresponding position feedback links increases system complexity and cost.
• Image accuracy may be reduced due to the influence of scanning motion accuracy, which ultimately affects measurement accuracy.
Line array camera selection
Calculate resolution: divide the width by the minimum detection accuracy to get the pixels required for each line;
Determine pixel accuracy: divide the width by the number of pixels to get the actual detection accuracy;
Determine line frequency: divide the length of movement speed per second by the pixel accuracy to get the number of scanned lines per second;
Select the camera based on the above values. For example, if the width is 1600 mm, the accuracy is 1 mm, and the movement speed is 22000 mm/s;
Resolution: 1600/1=1600 pixels, at least 2000 pixels, select a 2k camera 1600/2048=0.8
Actual accuracy: 22000mm/0.8mm=27.5KHz, the camera should be a 2048 pixel 28kHz camera.